Types of Forex Regulations
Summary: To build confidence and attract high-value clients you’ll need to have a license. This tutorial cuts through the complexities of forex regulations, assisting you in selecting the appropriate one (such as CySEC, FCA, or Mauritius FSC) to optimize your brokerage's potential.
The forex market thrives on competition, and attracting clients requires trust and transparency. Earning a reputable forex broker license is crucial in establishing credibility and attracting high-value traders.
But what are the differences between forex regulators? There’s a sea of options out there like CySEC, Mauritius, FCA, Belize, Seychelles and more. What should you pick?
In this article we’ll be talking about what’s offshore, the political system, and what advantages you have by being a regulated broker. Read along!
Who are financial regulators?
Financial regulators serve as watchdogs in the financial sector. These government authorities or independent entities (such as CySEC or the Mauritius FSC) establish the regulations for financial companies, including forex brokers. Their main purpose is to:
- Protect Investors: They put protections in place to avoid fraudulent activity and guarantee that traders are treated fairly.
- Maintain Market Stability: Regulations increase transparency and prevent manipulation, resulting in a healthy and stable trading environment.
- Promote Fair Competition: A clear set of guidelines levels the playing field for all forex brokers.
This results in various advantages for you as a licensed broker:
- Enhanced Credibility: A recognized forex broker license displays your dedication to compliance and ethical company practices. This builds confidence with potential clients looking for a secure trading environment.
- Access to a Larger Client Pool: Many respected organizations and wealthy people prefer to trade with regulated brokers. A license allows access to this valuable business niche.
- Reduced Operational Risk: Regulations frequently give a foundation for effective risk management techniques, which may reduce operational risks within your brokerage.
Why Opt for a Regulated Brokerage?
Let’s address the fundamental question: regulated vs. unregulated broker?
While working as an unregulated broker may appear appealing owing to possible cost savings or a lack of regulation, the hazards significantly outweigh the advantages. Here’s why taking the regulated road is a strategic decision:
- Mitigating Reputational Risks: Even a single occurrence with an unlicensed broker can harm your reputation and turn off customers. A license demonstrates your dedication to ethical procedures.
- Building Trust with Partners: Many liquidity providers and payment processors prefer to deal with licensed brokers. A license allows you easier access to essential associations.
- Keeping ahead of the curve: Regulatory environments are always changing. A license guarantees that you operate within the legal framework and are prepared for future changes.
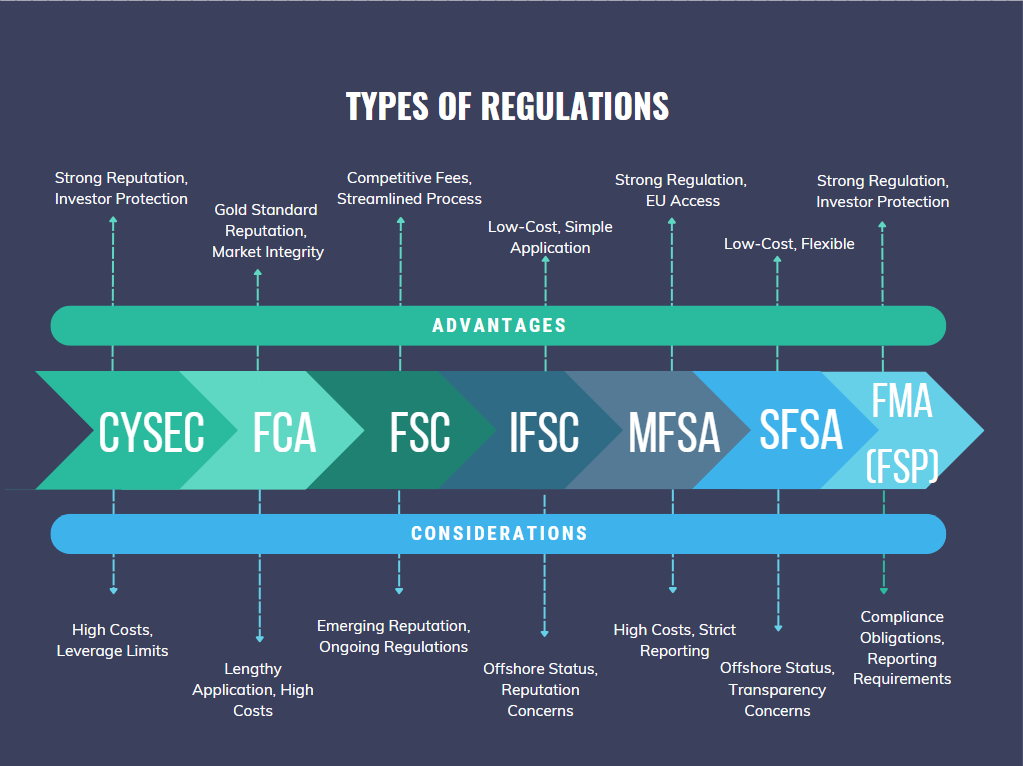
Types of Forex licenses
CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission)
CySEC, Cyprus’ regulatory organization, provides a respected and highly recognized license within the forex business. Its stringent compliance rules and control measures instil confidence in both brokers and traders.
Obtaining a CySEC license provides access to the European market, which may considerably strengthen a brokerage’s reputation and client base. Furthermore, being licensed by CySEC displays a dedication to openness and investor safety, which may attract high-value traders looking for a reliable brokerage.
However, obtaining a CySEC license implies a rigorous application procedure and adherence to tight regulatory standards. As a broker, you should be prepared for rigorous examination and continuing monitoring, which may result in increased operating expenses and administrative hassles.
FCA (Financial Conduct Authority – UK)
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom is well-known for its strong regulatory structure and strict monitoring of financial institutions. Brokers regulated by the FCA earn credibility and confidence from investors because of the regulator’s reputation for enforcing strong standards of conduct and consumer protection.
An FCA license provides access to the European market while also demonstrating compliance with stringent regulatory criteria, which improves a brokerage’s reputation and consumer appeal. Furthermore, the FCA offers significant support and guidance to regulated firms to ensure continuing compliance with regulatory requirements.
Obtaining an FCA license takes a lengthy application procedure and strict adherence to compliance rules, which can take a substantial amount of time and money. Brokers should also be prepared to face continual regulatory monitoring and scrutiny, which may limit operating flexibility.
Mauritius Financial Services Commission (FSC)
Mauritius has emerged as an appealing jurisdiction for forex brokers looking for a trustworthy regulatory framework paired with attractive tax breaks. Its regulatory authority, the Financial Services Commission (FSC), provides a simple licensing process and a business-friendly regulatory environment.
Mauritius-licensed brokers can take advantage of tax breaks, such as lower corporation tax rates and income exemptions. Furthermore, the jurisdiction’s political stability and solid legal framework ensure a safe working environment for financial services enterprises.
Despite these benefits, as a broker, you should be aware of Mauritius’ increasing regulatory requirements and the necessity to be compliant with international norms. The jurisdiction’s reputation is still growing, and continuing legislative changes may have an influence on future licensing conditions.
International Financial Services Commission of Belize (IFSC)
Belize has emerged as a notable offshore destination for forex brokers looking for a low-cost regulatory environment with simple licensing requirements. The International Financial Services Commission (IFSC) regulates financial service companies in Belize, with a simple application procedure and a favorable tax system.
Brokers licensed in Belize benefit from lower capital requirements and reduced regulatory burdens compared to more established jurisdictions. The IFSC’s flexible approach to regulation allows brokers to operate with greater autonomy and efficiency.
However, you should be mindful of the perceptions surrounding offshore jurisdictions and how they may affect your brokerage’s image. While Belize has several benefits, brokers must verify compliance with international standards and transparency regulations to retain credibility and confidence with customers.
Malta Financial Services Authority (MFSA)
Malta has positioned itself as a major financial services hub in the European Union, with a strong regulatory framework and access to a huge market. The Malta Financial Services Authority (MFSA) regulates financial services enterprises in Malta, guaranteeing compliance with EU rules and worldwide standards.
Brokers licensed in Malta benefit from EU membership, which allows them to provide services throughout the European Economic Area (EEA). The jurisdiction’s reputation for strong regulation and investor protection boosts a brokerage’s credibility and appeal.
Brokers should be prepared for strict compliance standards and continuing MFSA supervision. Malta enforces stringent reporting and disclosure requirements on regulated organizations, which could require substantial resources and administrative efforts toward compliance.
Seychelles Financial Services Authority (SFSA)
The Seychelles Financial Services Authority (SFSA) provides a flexible regulatory environment for forex brokers seeking low-cost licensing alternatives. Seychelles has become a popular offshore jurisdiction due to its cheap capital requirements and minimum reporting duties.
Brokers licensed in Seychelles benefit from a simpler application procedure and lower regulatory requirements, allowing for faster and more efficient market entrance. The jurisdiction’s reputation for regulatory flexibility attracts to brokers looking for operational independence and autonomy.
As a broker, you should be cautious while working in offshore countries such as Seychelles. While the regulatory system has certain benefits, it may generate worries among investors about transparency and investor protection. Before deciding on Seychelles as your regulatory jurisdiction, you should carefully analyze the trade-offs and the potential influence on your reputation and customer relationships.
Financial Services Provider (FSP) and Financial Markets Authority (FMA) – New Zealand
In New Zealand, the FSP (Financial Service Provider) and FMA (Financial Markets Authority) are two regulatory entities that govern financial services, including forex trading.
Previously, financial service providers, including forex brokers, needed to register with the FSP in order to operate lawfully in New Zealand. However, after the adoption of the Financial Markets Conduct Act in 2013, FSP registration has been replaced by FMA-supervised licensing requirements. The FMA licenses and regulates financial service firms, guaranteeing regulatory compliance and investor protection. As a result, although FSP registration was the prior regulatory framework, FMA license is now the principal regulatory mechanism for forex brokers operating in New Zealand.
In essence, FMA is the regulator, and FSP is the license issued by the FMA.
Forex brokers in New Zealand must be licensed by the FMA. To receive a license, an entity must register as a Financial Service Provider (FSP), which entails satisfying certain capital adequacy standards and following FMA rules.
Brokers should, however, be aware of the FSP regime’s compliance obligations and verify that regulatory criteria are met. The FMA imposes stringent regulations on financial service providers, including continuing reporting and disclosure requirements, which may entail additional resources and administrative efforts.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct jurisdiction for your forex brokerage is an important step that must be carefully considered. Before beginning the application process, you should conduct an extensive study on regulatory requirements and evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each jurisdiction in relation to your company goals.
Each regulatory body has unique benefits and problems, ranging from CySEC’s strong regulatory structure to Belize’s attractive tax climate and the FCA’s respected monitoring.
Whether you want to boost credibility, extend market reach, or improve operational efficiency, selecting the correct regulatory environment is critical to achieving long-term success in the forex sector.





